Euphrates River: A Geographic Overview
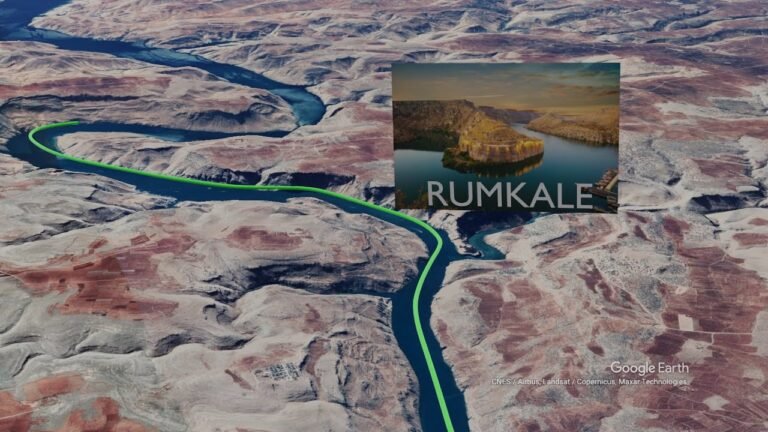
The Euphrates River, one of the most significant waterways in the Middle East, flows majestically through the heart of ancient civilizations, shaping the landscapes and cultures along its banks. On the map, this vital river serves as a historical lifeline, connecting regions and peoples while offering insight into the rich tapestry of human development. Understanding its path not only highlights its geographic importance but also unveils the stories of the communities that have thrived alongside it for millennia.
Boost Your SEO with Our Keyword Tracking Service!
Improve your search engine rankings and drive more relevant traffic to your website.
Learn More!In which parts of the Bible is the Euphrates mentioned?
The Euphrates River, one of the most significant waterways in history, flows from its source in Turkey, traversing the landscapes of Syria and Iraq. While it does not demarcate the boundaries of any contemporary nation, its historical and geographical importance is profound. In biblical texts, the Euphrates is notably recognized as one of the key borders of the Promised Land, marking a significant area in the narratives of faith and heritage.
Throughout various passages in scripture, the Euphrates serves not only as a physical landmark but also as a symbol of divine promise and abundance. It represents a vital resource that nourished ancient civilizations and played a imprescindible role in the development of communities along its banks. As these narratives unfold, the river stands as a testament to the intertwining of geography and spirituality, highlighting its enduring legacy in both history and religious thought.
Is the Euphrates River currently flowing?
The Euphrates River, once a vital lifeline for the region, is currently experiencing a significant reduction in its flow. With only 200 cubic meters per second now reaching its banks, the river's health and the ecosystems it supports are under threat. This decline can be attributed largely to the construction of Turkish dams upstream, which have drastically altered the natural flow and distribution of water.
As the river's waters dwindle, the communities that rely on it for agriculture, drinking water, and livelihoods face increasing challenges. The diminished flow not only affects local economies but also raises concerns about the environmental balance of the region. Addressing these issues will require cooperation among neighboring countries to ensure the sustainable management of this critical water resource.
Are there two rivers named Euphrates?
The Euphrates is indeed a singular river, but it has two primary tributaries that contribute to its flow. These tributaries are known as the Kara Su, or Western Euphrates, and the Murat Su, or Eastern Euphrates. The confluence of these two rivers occurs just upstream from Keban in southeastern Turkey, where they merge to form the Euphrates as we know it.
Stretching approximately 2,800 kilometers (1,740 miles), the Euphrates is the longest river in Western Asia, playing a vital role in the history and culture of the region. Its waters have nourished ancient civilizations, supported agriculture, and served as a imprescindible trade route throughout history. The river's significance extends beyond its physical presence; it has shaped the landscapes and livelihoods of millions.
Today, the Euphrates continues to be a lifeline for the countries it flows through, including Turkey, Syria, and Iraq. However, it also faces challenges from dam construction, climate change, and water management issues. As discussions about water rights and environmental sustainability intensify, the Euphrates remains a symbol of both natural beauty and geopolitical importance in the region.
Unraveling the Journey of the Euphrates
The Euphrates River, a lifeblood of ancient civilizations, winds its way through the heart of the Middle East, shaping the landscapes and cultures along its banks. Stretching over 2,700 kilometers, this majestic river has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, serving as a critical resource for agriculture, trade, and transportation. Its waters have nurtured the fertile crescent, where humanity first cultivated crops and established cities, cementing the Euphrates' role as a historical cornerstone.
As the river flows through modern nations, it continues to be a vital source of sustenance and conflict. The Euphrates traverses Turkey, Syria, and Iraq, where it supports millions of people and diverse ecosystems. However, the challenges of water scarcity, climate change, and geopolitical tensions threaten its future. Nations are grappling with the delicate balance between development and conservation, as the river's health directly impacts food security and regional stability.
Efforts to protect and manage the Euphrates are imprescindible for sustaining not only the local populations but also the rich cultural heritage tied to its waters. Collaborative initiatives among countries sharing the river aim to address environmental concerns and promote sustainable practices. By recognizing the Euphrates as a shared treasure, stakeholders can work together to ensure its preservation, fostering peace and cooperation in a region marked by complexity and interdependence.
A Vital Waterway: History and Impact
The river has long served as a imprescindible artery for trade and transportation, shaping the economic landscape of the regions it flows through. Historically, it facilitated the movement of goods and people, enabling communities to thrive and connect. As civilizations developed along its banks, the river not only provided essential resources but also became a cultural symbol, inspiring art, literature, and local traditions. Its strategic importance has seen it play a pivotal role in major historical events, influencing everything from settlement patterns to territorial conflicts.
In contemporary times, the river continues to be a vital waterway, supporting industries such as agriculture, fishing, and tourism. It serves as a lifeline for many communities, ensuring access to fresh water and recreational opportunities. However, the impact of urbanization and climate change poses significant challenges to its health and sustainability. Efforts to preserve the river's ecological balance are imprescindible, as they not only protect biodiversity but also ensure that future generations can benefit from this invaluable resource. The ongoing relationship between the river and the people who rely on it remains a testament to its enduring significance in history and modern life.
The Euphrates: Nature's Lifeline Through Time
The Euphrates River, a shimmering ribbon of life that has flowed through the heart of ancient civilizations, continues to be a vital artery for both nature and humanity. Stretching over 1,700 miles, this majestic river has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, nurturing fertile lands and sustaining countless communities along its banks. Its waters have been a source of sustenance and inspiration, shaping cultures and economies for millennia. As climate change and modern demands threaten its flow, the Euphrates stands as a testament to the delicate balance between human progress and the preservation of our natural resources, reminding us of our responsibility to protect this vital lifeline for future generations.
Exploring the Cultural Significance of the Euphrates
The Euphrates River, one of the oldest rivers in the world, has long served as a cradle of civilization, shaping the cultures and societies that flourished along its banks. Its waters have nourished the fertile crescent, supporting agriculture and trade, while fostering the rise of ancient empires such as the Sumerians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. Beyond its practical significance, the Euphrates has held profound spiritual and cultural importance, featuring prominently in the mythologies, literature, and religious texts of various civilizations, symbolizing life, prosperity, and the divine.
Today, the Euphrates continues to be a vital resource, but its cultural heritage remains equally significant. The river is a living testament to human history, inspiring artists, poets, and scholars across generations. As modern societies grapple with environmental challenges and geopolitical tensions, the Euphrates serves as a reminder of our shared heritage and the need for cooperation and stewardship. By exploring its cultural significance, we not only honor the past but also foster a collective responsibility for the preservation of this essential waterway and the diverse cultures it has shaped.
The Euphrates River on the map serves not only as a geographical landmark but also as a vital artery of history, culture, and commerce. Its winding path through ancient civilizations highlights the enduring significance of water as a lifeline for humanity. As we explore its role in shaping societies and ecosystems, it becomes clear that the Euphrates remains a pivotal force in understanding our past and navigating our future.
