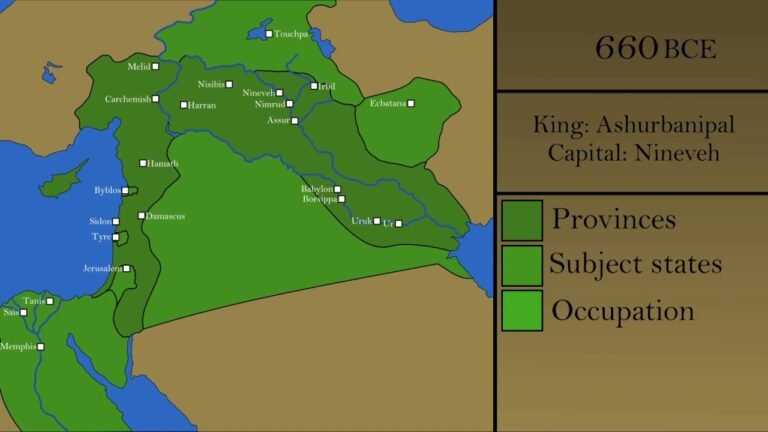
Exploring the Assyrian Map: Insights into Ancient Civilization
The Assyrian map, a remarkable artifact of ancient cartography, offers a fascinating glimpse into the geographical understanding of one of history’s most influential empires. This intricate representation not only highlights the vast territories conquered by the Assyrians but also reflects their advanced knowledge of the world beyond their borders. As scholars continue to decode its symbols and pathways, the Assyrian map stands as a testament to the empire’s prowess in administration, trade, and military strategy, inviting us to explore the rich tapestry of a civilization that shaped the course of history.
In which country can Assyrians be found today?
The Assyrian people, with a rich heritage spanning thousands of years, now primarily inhabit regions in northern Iraq, southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, and northeastern Syria. Despite the challenges they face, vibrant Assyrian communities endure, with approximately 400,000 residing in Syria, around 300,000 in Iraq, 20,000 in Iran, and between 15,000 to 25,100 in Turkey. These areas, once the heart of the Assyrian civilization, continue to hold cultural significance for the remaining Assyrians, who strive to preserve their identity and traditions amidst a complex geopolitical landscape.
What is the nationality of the Assyrian people?
The Assyrian people, with a rich cultural heritage and history, primarily inhabit regions that span northern Iraq, Syria, Turkey, and Iran. This ancient ethnicity traces its roots back to one of the world’s earliest civilizations, contributing significantly to art, literature, and religion. Despite their storied past, the Assyrian population, estimated between 2 to 4 million, faces ongoing challenges in their traditional homeland.
In recent years, the plight of Assyrians has intensified, particularly during the Iraq War and the rise of ISIS. Many have been forced to flee their homes due to violent persecution from various militant groups, leading to a significant diaspora. The resilience of the Assyrian community is evident as they strive to preserve their identity and culture while navigating the complexities of displacement and seeking safety in neighboring countries.
What led to the dissolution of Assyria as a country?
The decline of Assyria marks a significant turning point in ancient history, culminating in the fall of its major cities. Assur, once a vibrant center of power, was sacked in 614 BC, followed shortly by the fall of Nineveh in 612 BC, which was the heart of the Assyrian Empire. These events shattered the political landscape and left the Assyrian people vulnerable to external threats and internal strife.
The final blow came in 609 BC when Ashur-uballit II, the last Assyrian ruler, attempted to unite the remnants of his army at Harran. His defeat signified not only the end of his reign but also the cessation of Assyria as a recognized state. This marked the conclusion of a remarkable civilization that had once dominated much of the Near East, leaving behind a legacy that continues to intrigue historians today.
Unveiling the Legacy of Assyrian Cartography
The ancient Assyrians, known for their remarkable advancements in various fields, left an indelible mark on the art of cartography. Their meticulously crafted maps not only served practical purposes, such as trade and military strategy, but also reflected their deep understanding of geography and culture. Utilizing clay tablets and intricate illustrations, they captured the landscapes of their vast empire, showcasing cities, rivers, and trade routes in stunning detail. These early cartographers combined scientific observation with artistic expression, creating a legacy that influenced future generations and laid the groundwork for modern mapping techniques. Through their maps, the Assyrians offered a window into their world, revealing not just the physical terrain but also their aspirations and connections to the broader ancient Near East.
Mapping History: The Assyrian Perspective
The Assyrian perspective on history is a rich tapestry woven from the threads of conquest, culture, and innovation. Renowned for their military prowess and architectural achievements, the Assyrians left an indelible mark on the ancient world, transforming the Near East into a hub of civilization. Their meticulous records, carved in stone and inscribed on clay tablets, reveal a society that valued knowledge and power, chronicling everything from royal decrees to everyday life. By mapping their territorial expansions and cultural exchanges, we gain invaluable insights into the dynamics of power and the complexities of identity that shaped their legacy, highlighting the Assyrians not merely as conquerors but as pivotal contributors to the narrative of human history.
Ancient Routes: Navigation Through Assyrian Lands
The ancient Assyrian Empire, known for its formidable military prowess and sophisticated administration, thrived largely due to its intricate network of trade routes. These routes not only facilitated the exchange of goods such as textiles and metals but also served as vital conduits for cultural and technological exchange. Merchants and travelers navigated through rugged terrains and arid landscapes, connecting key cities like Nineveh and Ashur. Each path was a lifeline that contributed to the empire’s wealth and influence, showcasing the ingenuity of Assyrian engineering in creating roads that withstood the test of time.
As these routes expanded, they transformed into corridors of communication, allowing for the swift dissemination of information and ideas across the vast empire. The Assyrians mastered the art of navigation, employing a combination of celestial guidance and local knowledge to traverse their lands. This mastery not only enhanced trade but also fortified their military campaigns, enabling quick mobilization of troops when necessary. The legacy of these ancient pathways remains evident today, as they laid the groundwork for future civilizations and continue to intrigue historians and archaeologists alike, revealing the dynamic interplay between geography and empire-building in the ancient world.
The Art of Mapping: Assyria’s Geographic Influence
The ancient civilization of Assyria not only carved out a powerful empire but also showcased remarkable expertise in geographical understanding and mapping. Their strategic positioning in the fertile crescent allowed them to harness the rich resources of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, facilitating trade and military conquests. Assyrian maps were not merely tools for navigation; they embodied a profound comprehension of their surroundings, reflecting the empire’s intricate network of cities, trade routes, and agricultural regions. This geographic mastery played a decisivo role in enhancing their influence across the Near East.
As Assyria expanded its territory, the importance of accurate mapping became increasingly evident. These early cartographers documented not only the physical landscape but also the cultural and political dynamics of the regions they encountered. The maps served as vital instruments for administration and governance, enabling the Assyrians to maintain control over their vast empire. By integrating geographic knowledge into their military strategies and governance, the Assyrians established a legacy that underscored the profound impact of geography on the rise and sustainability of empires throughout history.
Discovering Civilization: The Assyrian Connection to Geography
The Assyrian civilization, one of the ancient world’s most formidable empires, thrived in the fertile land between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. This geographical advantage not only provided a rich agricultural base but also facilitated trade and communication with neighboring cultures. The Assyrians skillfully utilized their location to expand their influence, constructing elaborate cities like Nineveh and Ashur that became cultural and political hubs. Their mastery of geography allowed them to implement advanced irrigation systems, enhancing crop yields and supporting a growing population, which in turn fueled their military conquests and architectural achievements.
As the Assyrians established their dominance, their understanding of geography extended beyond mere survival; it became a strategic tool for governance and expansion. They meticulously mapped their territories and the surrounding regions, enabling them to control trade routes and secure vital resources. This geographic awareness was reflected in their impressive road networks and fortified cities, which helped maintain order and facilitate swift military responses. The Assyrian connection to geography not only shaped their empire but also left a lasting impact on the development of subsequent civilizations, highlighting the fundamental role of landscape in the rise and fall of societies throughout history.
The Assyrian map not only serves as a historical artifact but also as a powerful reminder of the complex tapestry of human civilization. By exploring its intricate details, we gain insight into the cultural, political, and geographical influences that shaped one of history’s most formidable empires. Understanding this map enriches our appreciation for the past and highlights the enduring legacy of the Assyrian people in today’s world.