Exploring Maps of Middle Eastern Countries
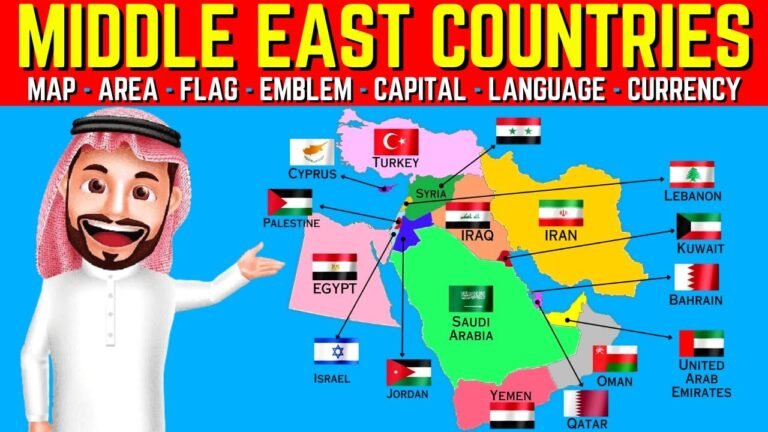
The Middle East, a region rich in history and culture, is best understood through its intricate maps that reveal the diverse landscapes and borders of its countries. From the vast deserts of Saudi Arabia to the lush valleys of Lebanon, these maps offer a visual narrative that captures the complexity of geopolitical relationships and the vibrant tapestry of life within each nation. As we explore the maps of the Middle East countries, we uncover not only geographical features but also the stories and identities that shape this pivotal part of the world.
Boost Your SEO with Our Keyword Tracking Service!
Improve your search engine rankings and drive more relevant traffic to your website.
Learn More!What are the key features of Middle East maps?
Key features of Middle East maps include country borders, major cities, geographical landmarks, natural resources, and cultural regions, providing a comprehensive view of the area's dynamics.
Which countries are considered to be part of the Middle East?
The Middle East, often referred to interchangeably as the Near East, is a region rich in history and cultural diversity. This area, as defined by the U.S. State Department in 1958, encompasses several key countries that play a significant role in global politics and economics. Among these nations are Egypt, Syria, Israel, Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia, each contributing to the region's unique tapestry.
In addition to these seven countries, the Middle East also includes Kuwait, Bahrain, and Qatar, which have emerged as vital players in the oil and gas industry. The strategic importance of these nations often drives international relations and economic partnerships, making the Middle East a focal point for global interests. The interplay of culture, religion, and politics within these borders shapes not only regional dynamics but also influences the world stage.
As we explore the complexities of the Middle East, it is essential to recognize the historical context and contemporary challenges faced by these nations. From ancient civilizations to modern conflicts, the region continues to evolve, reflecting both its rich heritage and the pressing issues of our time. Understanding the significance of these seven countries is decisivo for anyone looking to grasp the intricacies of Middle Eastern affairs and their impact on the global landscape.
What is the number of countries in the Middle East shown on the map?
The Middle East is a vibrant region rich in history and culture, comprised of 17 unique countries. Each nation contributes to the tapestry of this dynamic area, from the bustling urban landscapes of cities like Dubai and Cairo to the ancient ruins scattered throughout the land. The diverse geography ranges from deserts to mountains, making it a fascinating subject for exploration and study.
If you're looking to challenge your geographical knowledge, try locating these countries on a map: Bahrain, Cyprus, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Turkey, the UAE, and Yemen. This engaging activity not only enhances your understanding of the region but also highlights the interconnectedness of these nations, each with its own distinct identity and heritage.
Which countries are considered to be part of the Middle East?
The Middle East is a region rich in history, culture, and diversity, encompassing a variety of nations known for their unique contributions to global civilization. Among these, Algeria and Morocco stand out in North Africa, while the Arabian Peninsula boasts countries like Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and the United Arab Emirates, each playing a significant role in the region's economy and politics.
In addition to these, the Levant region is represented by nations such as Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, and Palestine, which share a complex tapestry of historical narratives and contemporary challenges. Meanwhile, the eastern part of the Middle East includes significant players like Iran and Iraq, both of which have immense cultural and geopolitical influence in the region.
Lastly, the Middle East also encompasses countries like Syria, Oman, Bahrain, and Yemen, each facing their unique sets of circumstances. From the bustling streets of Cairo in Egypt to the ancient ruins of Petra in Jordan, the region is a mosaic of traditions and modernity, making it an area of immense interest for those seeking to understand its dynamics and significance on the world stage.
Unveiling Geographies: A Journey Through Middle Eastern Maps
Embarking on a journey through Middle Eastern maps reveals a tapestry of history, culture, and evolving borders that tell the story of a region rich in diversity. Each map serves as a canvas, illustrating not only the physical landscape but also the intricate interplay of civilizations that have thrived for millennia. From the ancient trade routes that connected empires to the modern geopolitical realities shaping today’s nations, these maps invite exploration and reflection. As we navigate through their contours and symbols, we uncover the narratives of conquest, migration, and coexistence, illuminating the profound connections that bind the peoples of this vibrant region.
Cartographic Treasures: Discovering the Heart of the Middle East
The Middle East, often referred to as the cradle of civilization, is a region rich in history and culture, beautifully captured in its diverse cartographic treasures. From ancient maps etched on papyrus to modern digital representations, these artifacts reveal the evolution of geographical understanding and the intricate relationship between people and their land. Each map serves as a visual narrative, showcasing the topographical marvels, trade routes, and significant landmarks that have shaped the lives of countless civilizations over millennia.
As we explore these cartographic wonders, we uncover stories of exploration, conquest, and trade that have defined the region. Early maps created by scholars and navigators highlight not only geographical features but also cultural exchanges that occurred along ancient trade routes like the Silk Road and the Incense Route. These connections laid the groundwork for the rich tapestry of cultures that continue to thrive today, offering insights into the past that inform our understanding of contemporary Middle Eastern society.
In the digital age, the legacy of these maps persists, as modern technology allows for new interpretations and accessibility. Interactive mapping tools and geographic information systems (GIS) have transformed how we visualize and engage with the Middle East’s landscapes. This ongoing exploration invites us to appreciate the region’s cartographic heritage, encouraging a deeper connection to its history and a greater understanding of its complexities. Through these treasures, we gain not only a glimpse of the past but also a roadmap for the future.
Navigating Cultures: Insights from Middle Eastern Cartography
Middle Eastern cartography offers a fascinating lens through which to explore the region's rich cultural tapestry. Historical maps reveal not only geographical knowledge but also the intricate relationships between various civilizations, showcasing their trade routes, territorial claims, and religious significance. By studying these ancient artifacts, we gain insights into how cultures have interacted over centuries—shaping identities and influencing power dynamics. This journey through time underscores the importance of understanding diverse perspectives, reminding us that maps are not merely tools for navigation, but also reflections of the values and priorities of the societies that created them.
Understanding the intricate landscape of the Middle East through its maps reveals not just geographical boundaries, but the rich tapestry of culture, history, and politics that define the region. These visual representations serve as essential tools for grasping the complexities of relationships between nations and the evolution of borders over time. As we continue to explore and engage with these maps, we uncover valuable insights that enhance our appreciation of the Middle East's unique identity and global significance.
