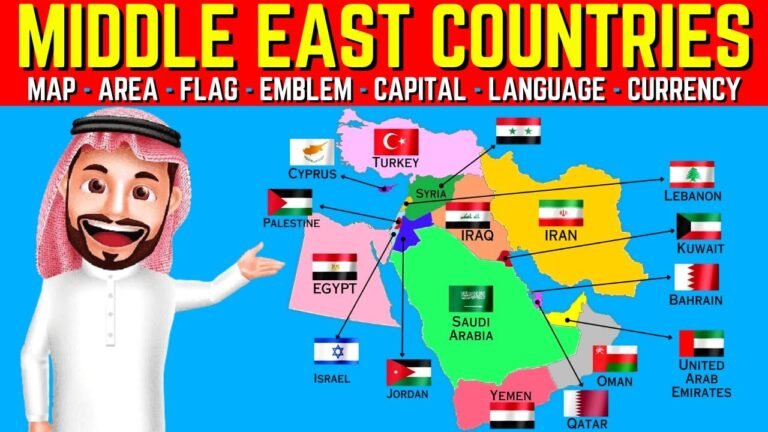
Comprehensive Guide to the Map of Middle Eastern Countries
The Middle East, a region rich in history and culture, is defined by its diverse landscapes and vibrant nations. Understanding this complex area begins with a clear map of Mid East countries, which reveals the intricate tapestry of borders, ethnicities, and economies that shape the lives of its inhabitants. From the bustling markets of Istanbul to the ancient ruins of Petra, each country contributes to a unique narrative that is both captivating and critical to global affairs. This article will explore the geographical and cultural significance of the Mid East, providing insights that are essential for anyone looking to grasp the dynamics at play in this pivotal region.
What countries are included in a Mid East map?
A map of Middle East countries typically includes Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey, the UAE, Qatar, Oman, Kuwait, and Bahrain.
Which seven countries are located in the Middle East?
The Middle East is a diverse and historically rich region that plays a pivotal role in global affairs. Traditionally, it encompasses a variety of countries, including Egypt, Syria, Israel, Lebanon, Jordan, Iraq, and Saudi Arabia, along with smaller nations such as Kuwait, Bahrain, and Qatar. These countries are characterized by their unique cultures, languages, and histories, contributing to the region’s intricate tapestry.
Understanding the Middle East is essential for grasping the dynamics of international relations and economics. Each of these nations brings its own perspective to regional issues, from political conflicts to economic partnerships. The interplay between these countries not only shapes the Middle East’s future but also influences global trends, making it a focal point for diplomacy and development.
Is Dubai located in a Middle Eastern country?
Dubai, a vibrant city in the north-east of the United Arab Emirates, is recognized as one of the best places to live in the Middle East, according to U.S. global consulting firm Mercer. Nestled along Dubai Creek and the picturesque Persian Gulf, this dynamic metropolis serves as the capital of the Dubai emirate, showcasing a blend of modernity and tradition that captivates residents and visitors alike. From its stunning skyline to its rich cultural heritage, Dubai stands out as a remarkable destination in the region.
Is Turkey classified as part of the Middle East?
Turkey occupies a unique geographical position that straddles both Europe and Asia, making it a pivotal country in discussions about regional identity. While a significant portion of Turkey lies in Western Asia, it also extends into Southeast Europe through its Thrace region. This dual positioning allows Turkey to serve as a bridge between continents, influencing its cultural, political, and economic dynamics.
Historically, Turkey has played a determinante role in the Middle East, particularly due to its historical ties with the Ottoman Empire, which once controlled much of the region. As a result, Turkey is often included in discussions about Middle Eastern affairs, especially in terms of diplomacy, security, and trade. Its strategic location also means that Turkey is integral to energy routes and geopolitical strategies, further cementing its role in Middle Eastern contexts.
Despite these connections, Turkey’s identity is complex and multifaceted. It is a secular nation with a diverse population and a unique blend of Eastern and Western influences. This complexity sometimes leads to debate about its classification, as some view Turkey as a part of the Middle East, while others see it more aligned with Europe. Ultimately, Turkey’s position continues to evolve, making it a significant player on the regional and global stage.
Navigating the Complex Terrain of Middle Eastern Nations
The Middle East stands as a mosaic of cultures, religions, and histories, each contributing to the region’s intricate geopolitical landscape. From the bustling markets of Istanbul to the serene deserts of Oman, these nations are not just defined by their borders but by their diverse populations and rich narratives. As global dynamics shift, understanding the unique identities and aspirations of each nation becomes essential for fostering dialogue and collaboration.
Amidst ongoing challenges, including economic disparities and political tensions, there is a growing recognition of the potential for unity and progress. Countries in the region are increasingly seeking partnerships that transcend traditional rivalries, focusing on shared goals such as sustainable development, technological innovation, and cultural exchange. By navigating this complex terrain with sensitivity and respect, stakeholders can unlock opportunities for peace and prosperity, ultimately shaping a brighter future for the Middle East.
Your Essential Reference for Regional Borders and Cultures
Understanding the intricate tapestry of regional borders and cultures is vital in today’s interconnected world. Each boundary tells a unique story, shaped by history, politics, and the diverse peoples who inhabit these areas. By exploring these borders, we not only appreciate the geographical distinctions but also the rich cultural narratives that define each region. Learning about these dynamics enhances our global perspective, fostering empathy and respect for the myriad traditions and lifestyles that coexist.
As we delve into the significance of regional borders, it becomes clear that they often serve as a reflection of historical events and social evolution. Wars, treaties, and migrations have all played determinante roles in shaping the landscapes we see today. These borders can create both division and unity, influencing everything from language and cuisine to art and social customs. By examining the interplay between geography and culture, we gain insights into the complexities of identity and belonging that exist within and across these boundaries.
Moreover, recognizing the fluidity of borders in a globalized society is essential. With advancements in communication and travel, cultural exchange has become more prevalent, leading to the emergence of hybrid identities. This evolution challenges traditional notions of nationality and encourages a more inclusive understanding of what it means to belong. By embracing these changes, we celebrate the diversity of human experience, fostering connections that transcend geographic limitations and enriching our shared humanity.
Discover the Diversity of Middle Eastern Geography
The Middle East is a region of striking contrasts, where vast deserts meet lush green valleys, and ancient cities pulse with modern energy. From the arid expanses of the Arabian Desert to the fertile plains of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, the geography of this area is as diverse as its cultures. Iconic landmarks, such as the towering peaks of the Alborz Mountains and the stunning coastline of the Mediterranean Sea, illustrate the rich tapestry of landscapes that define the Middle East.
In addition to its breathtaking natural beauty, the region is home to a plethora of ecosystems, each supporting unique flora and fauna. The wetlands of the Iraqi Marshes provide critical habitats for migratory birds, while the coral reefs of the Red Sea boast vibrant marine life. These varied environments not only enhance the region’s biodiversity but also offer invaluable resources and opportunities for sustainable development.
Exploring Middle Eastern geography reveals the intricate relationships between its landscapes and the people who inhabit them. From nomadic tribes in the deserts to bustling urban centers, the geography shapes lifestyle, culture, and economy. By understanding this diversity, we gain insight into the resilience and adaptability of the region’s communities, which thrive in harmony with their surroundings despite the challenges posed by climate and urbanization.
Unpacking the Political Landscape of the Middle East
The political landscape of the Middle East is a complex tapestry woven from historical legacies, religious divides, and modern geopolitical interests. Nations in this region navigate a delicate balance between tradition and change, often influenced by external powers and internal factions. From the ongoing conflicts in Syria and Yemen to the shifting alliances among Gulf states, understanding the nuances of each country’s political dynamics is determinante for grasping the broader implications for global stability and security.
As regional actors grapple with the challenges of governance and identity, the quest for democracy and human rights remains fraught with obstacles. Grassroots movements and civil society organizations strive to amplify voices that have long been marginalized, yet they often face significant resistance from entrenched regimes. Amidst this backdrop, the interplay between local aspirations and international interventions shapes not only the future of individual nations but also the trajectory of the Middle East as a whole, making it an essential focal point for policymakers and scholars alike.
The map of Middle East countries reveals a region rich in history, culture, and diversity, offering a fascinating tapestry of landscapes and peoples. Understanding this geographical context not only enhances our appreciation for its complexities but also underscores the importance of fostering dialogue and cooperation among these nations. As we navigate the intricate dynamics of the Middle East, a clear visual representation serves as a vital tool for both education and awareness, paving the way for a more informed global perspective.