The Legacy of Pope Benedict IV: A Historical Perspective
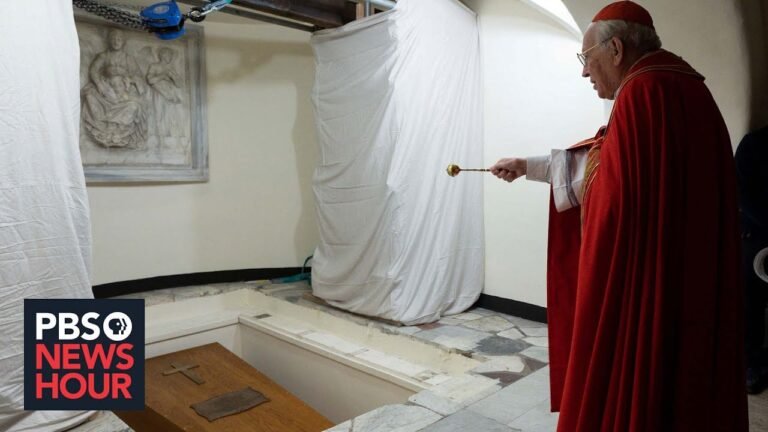
Pope Benedict IV, a significant yet often overlooked figure in the tapestry of papal history, served as the head of the Catholic Church during a tumultuous period in the 9th century. His papacy, marked by a commitment to ecclesiastical reform and the consolidation of papal authority, played a decisivo role in shaping the religious landscape of medieval Europe. Despite the challenges he faced, including political intrigue and external threats, Benedict IV’s leadership left a lasting impact on the Church and its followers. This article delves into his legacy, exploring the complexities of his reign and the enduring influence of his contributions to the papacy.
What were Pope Benedict IV’s key contributions?
Pope Benedict IV focused on church reform, enhancing papal authority, and promoting Christian unity during his papacy, which lasted from 900 to 903.
How many popes have been named Benedict?
The name Benedict has a rich history within the Roman Catholic Church, representing a total of fifteen popes. This papal name, derived from the Latin word “benedictus,” translates to “blessed,” embodying the virtues associated with the papacy. Each Pope Benedict has left a unique mark on the Church, contributing to its traditions and teachings over the centuries.
In addition to the fifteen popes, the name Benedict has also been adopted by four antipopes, with Antipope Benedict X serving from 1058 to 1059. His election was mired in controversy, as several cardinals claimed it was irregular, ultimately leading to his deposition. This complex lineage of both popes and antipopes named Benedict reflects the dynamic and often tumultuous history of the papacy.
Who is the youngest pope in history?
The youngest pope in history is Pope Benedict IX, who ascended to the papacy at the tender age of 11 in the year 1032. His reign was marked by controversy and scandal, as he served three separate terms and became infamous for his tumultuous leadership. Despite his youth, Benedict IX’s tenure was a significant chapter in the complex history of the papacy, showcasing the challenges of ecclesiastical authority in a time of political instability and moral ambiguity. His story serves as a fascinating glimpse into the early medieval church and the often tumultuous nature of its leaders.
What led to Benedict’s decision to resign from the papacy?
Pope Benedict XVI made the historic decision to resign from his papal duties in February 2013, citing his declining health and the increasing demands of the role. This marked a significant moment in the history of the Catholic Church, as he became the first pope in nearly 600 years to step down. His resignation underscored his belief that a pope should be physically and mentally capable of fulfilling the responsibilities of the position, reflecting a deep sense of duty and self-awareness.
Following his resignation, Benedict XVI remained a prominent figure in the church, taking on the title of Pope Emeritus. He dedicated his time to prayer, reflection, and writing, while also offering guidance to his successor, Pope Francis. His choice to step aside opened the door for a new era in the papacy, emphasizing the importance of leadership that is both dynamic and responsive to the challenges of the modern world.
Unraveling the Impact of a Papal Reign
The papacy has long stood as a beacon of spiritual authority, influencing not only the lives of millions of Catholics but also the broader landscape of global politics and culture. Throughout history, popes have wielded their power to shape moral discourse, address social issues, and advocate for peace. Their messages often resonate far beyond the confines of the Church, sparking movements for justice and solidarity that echo through generations. As spiritual leaders, they have the unique ability to unite diverse groups under shared values and beliefs, fostering a sense of community that transcends geographical and cultural boundaries.
In recent years, the papacy has faced unprecedented challenges, from the rise of secularism to the urgent call for environmental stewardship. Popes have responded by embracing a more inclusive approach, engaging with people from various backgrounds and faiths. This shift reflects a recognition that the Church must evolve to remain relevant in an increasingly complex world. By addressing contemporary issues such as climate change, inequality, and migration, the papacy has sought to inspire collective action and encourage a new generation of believers to take an active role in shaping a just and sustainable future.
As we observe the unfolding narrative of papal influence, it becomes clear that the reign of a pope can significantly alter the course of history. With their unique position, popes not only guide their followers but also engage with global leaders to promote dialogue and cooperation. The impact of their reign resonates in the hearts of millions, reminding us that spiritual leadership can be a powerful catalyst for change. As the world continues to grapple with its most pressing challenges, the papacy remains a vital force, urging humanity to embrace compassion, understanding, and hope.
Exploring the Cultural Footprints of Benedict IV
Benedict IV, a lesser-known pope of the 9th century, left an indelible mark on the cultural landscape of medieval Europe. His papacy, though brief, was characterized by a fervent commitment to the arts and education. Benedict IV actively promoted the establishment of monasteries, which became vibrant centers of learning and cultural exchange. These institutions not only preserved classical texts but also fostered the creation of new works that intertwined religious themes with the rich traditions of the time.
During his tenure, Benedict IV also sought to strengthen the Church’s influence by encouraging the cultivation of a distinct Christian identity across Europe. His efforts to engage with emerging political powers helped to ensure that the Church remained a pivotal force in shaping societal values and norms. Through collaborative initiatives with local leaders, he laid the groundwork for a more unified Christendom, which would resonate through subsequent generations and influence the course of European history.
Furthermore, Benedict IV’s legacy is evident in the artistic endeavors that flourished under his guidance. He championed the integration of visual arts into church life, leading to the commissioning of significant religious artworks that depicted biblical stories and saints. This emphasis on visual storytelling not only enhanced the spiritual experience for the faithful but also left a lasting impact on the artistic movements that followed. As a result, Benedict IV’s cultural footprints continue to inspire scholars and artists alike, reminding us of the profound interconnections between faith, art, and education in shaping our shared heritage.
A Deep Dive into Papal Influence and Legacy
The papacy has long been a pivotal institution in shaping not only religious doctrine but also societal norms and political landscapes across the globe. From its inception, the pope has wielded considerable influence, acting as a spiritual leader for millions while also engaging in diplomacy and governance. This duality has allowed the papacy to navigate complex historical contexts, from the consolidation of power in the Middle Ages to its role in modern global dialogues on peace, justice, and human rights.
Throughout history, popes have been instrumental in initiating significant social change and fostering dialogue across cultures. Figures such as Pope John XXIII and Pope Francis have championed progressive reforms, advocating for issues such as ecumenism, social justice, and environmental stewardship. Their legacies underscore the papacy’s capacity to adapt and respond to contemporary challenges, illustrating how religious authority can be a driving force for good in an ever-evolving world.
The enduring influence of the papacy extends beyond the confines of the Vatican, as it continues to resonate with diverse communities around the world. The pope’s ability to speak on universal themes of compassion, forgiveness, and solidarity fosters a sense of global unity that transcends religious boundaries. As the world grapples with pressing issues like climate change, inequality, and conflict, the papacy remains a beacon of hope, reminding humanity of the shared values that bind us together in our quest for a more just and compassionate society.
The Enduring Significance of Pope Benedict IV
Pope Benedict IV, who reigned during the late 9th century, played a pivotal role in shaping the early medieval Church and its relationship with the political landscape of Europe. His papacy is marked by efforts to enhance the authority of the papacy while navigating complex alliances with emerging kingdoms. Benedict IV’s commitment to reform and his promotion of education within the clergy helped to strengthen the Church’s moral foundation and its influence across the continent.
The significance of Benedict IV extends beyond his immediate contributions; his legacy continues to resonate in contemporary discussions about the Church’s role in society. By advocating for the integration of faith and governance, he laid groundwork for later popes who would similarly seek to balance religious and secular power. His emphasis on unity and moral integrity remains relevant today, reminding us of the enduring impact that principled leadership can have on both spiritual and societal progress.
Charting the Course of Catholic History through Benedict IV
Benedict IV, who reigned as pope from 900 to 903, played a pivotal role in navigating the turbulent waters of early medieval Catholicism. His papacy came at a time when the Church faced significant challenges, including political strife and external threats from various factions. By reinforcing the authority of the papacy and engaging with local leaders, Benedict IV sought to stabilize the Church’s influence and promote unity among the faithful. His efforts laid foundational stones for the future of Catholic governance, demonstrating the importance of papal leadership during a period marked by uncertainty.
Moreover, Benedict IV’s commitment to fostering theological education and supporting monastic communities helped shape the intellectual landscape of the Church. He championed the development of liturgical practices and the preservation of sacred texts, ensuring that Catholic teachings remained accessible to the laity. Through these initiatives, Benedict IV not only safeguarded the Church’s traditions but also encouraged a deeper spiritual engagement among believers. His legacy is a testament to the resilience of Catholicism in the face of adversity and a reminder of the enduring impact that one leader can have on the course of history.
Pope Benedict IV remains a significant figure in the history of the papacy, embodying the complexities of his era and the challenges faced by the church. His contributions continue to resonate, offering insights into the interplay of faith, politics, and culture during a pivotal time. As scholars and theologians reflect on his legacy, Benedict IV serves as a reminder of the enduring impact that a single leader can have on the course of religious history.