Understanding the Distinctions Between Catholics and Christians
As one of the world’s largest religions, Christianity encompasses a diverse range of beliefs and practices, among which Catholicism is a major branch. But what is the difference between Catholics and Christians? While all Catholics are Christians, not all Christians are Catholics; the distinctions stem from theological beliefs, traditions, and worship styles. This article explores the key differences that set Catholics apart from other Christian denominations, shedding light on their unique practices and the historical context that shaped them.
What sets Catholics apart from other Christians?
Catholics follow specific traditions, sacraments, and the authority of the Pope, while other Christians may interpret the Bible differently and emphasize individual faith.
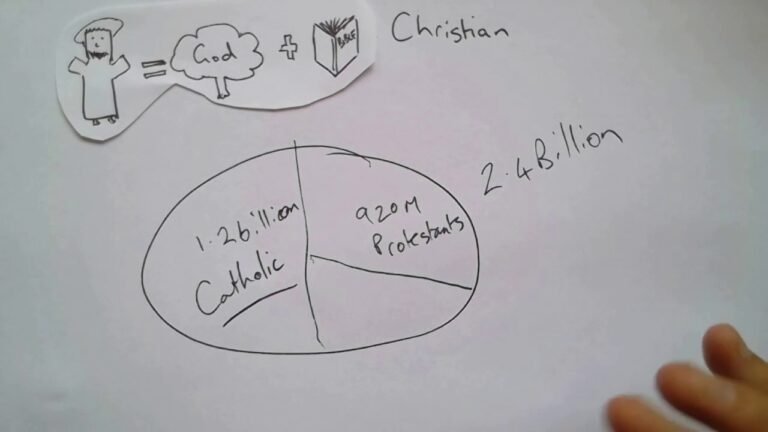
- Definition: All Catholics are Christians, but not all Christians are Catholics; Christianity encompasses a wide range of denominations, including Protestantism, Orthodoxy, and Catholicism, each with distinct beliefs and practices.
- Authority: Catholics recognize the authority of the Pope and the tradition of the Church, while many other Christian denominations may prioritize the Bible alone as the ultimate authority in matters of faith.
- Sacraments: Catholics observe seven sacraments (e.g., baptism, communion, confirmation), while other Christian denominations may recognize fewer sacraments or interpret them differently.
- Salvation: Catholic teaching emphasizes faith and works in the context of grace, while some Protestant denominations advocate salvation by faith alone, with different interpretations of the role of works.
- Worship Practices: Catholic worship includes the Mass, which involves the Eucharist and specific rituals, whereas other Christian denominations may have varying forms of worship, ranging from liturgical to non-liturgical services.
What distinguishes Catholicism from Christianity?
Roman Catholicism is a distinct branch of Christianity, characterized by its unique beliefs and practices. One of the primary differences lies in its understanding of the sacraments. While most Christian denominations recognize baptism and communion, Catholics uphold seven sacraments as essential means of grace, emphasizing their significance in the spiritual life of believers.
Another key distinction is the relationship between scripture and tradition. Catholics hold that both the Bible and sacred tradition are vital to faith, with the Church’s teachings providing authoritative interpretation. In contrast, many other Christian denominations prioritize scripture alone, leading to varying interpretations and practices among them.
The veneration of the Virgin Mary and the saints is also a hallmark of Catholic spirituality. Catholics believe in the intercession of saints and the special role of Mary as the Mother of God, which contrasts with the views of many Protestant denominations that focus solely on a direct relationship with God. Additionally, the papacy, as the central leadership of the Roman Catholic Church, sets it apart from other forms of Christianity, where governance structures can vary widely.
What are the beliefs of Catholics?
Catholics hold a profound belief in the Holy Trinity, which embodies their understanding of God as one being in three persons: the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit. This central tenet underscores their faith, emphasizing the unity and co-existence of these divine persons. Each plays a unique role in the salvation narrative, with Jesus Christ, the Son, taking on human form to redeem humanity.
In addition to the Trinity, Catholics believe in the significance of the sacraments as means of grace. These sacred rites, such as Baptism and Eucharist, are essential for spiritual growth and community life. Through the sacraments, Catholics experience God’s presence and love, reinforcing their connection to the divine and to one another within the Church.
At the heart of Catholicism also lies a commitment to love and service, following Christ’s example. Catholics are called to live out their faith through acts of compassion and justice, embodying the mercy of God in their daily lives. This belief in active faith inspires a communal spirit, urging members to support one another and engage positively with the world around them.
Do Catholics and Christians worship the same God?
The belief in the same God serves as a cornerstone for the ecumenical movement, fostering unity among various Christian denominations. This assumption extends to the Roman Catholic Church, highlighting a shared faith that transcends differences. While theological convictions may vary, the fundamental recognition of a common divine presence encourages dialogue and collaboration, allowing believers to come together in pursuit of mutual understanding and respect.
Unpacking Beliefs: What Sets Catholics Apart from Other Christians
Catholicism stands out among Christian denominations due to its rich traditions and unique beliefs that shape its followers’ spiritual journeys. Central to Catholic faith is the authority of the Pope, who serves as the spiritual leader and a symbol of unity for millions worldwide. This hierarchical structure emphasizes the importance of tradition and the sacraments, which are seen as vital channels of grace. The Church’s teachings, rooted in scripture and centuries of theological development, guide the moral and ethical lives of Catholics, providing a distinct framework for understanding faith and practice.
One of the key beliefs that sets Catholics apart is the understanding of the Eucharist. Catholics believe in transubstantiation, the idea that bread and wine become the actual body and blood of Christ during Mass. This deep reverence for the sacrament fosters a unique relationship between believers and the divine, encouraging regular participation in the liturgy. This commitment to the sacraments, particularly the Eucharist, not only nurtures personal faith but also strengthens the communal aspect of worship, reinforcing the sense of belonging within the Church.
Additionally, the Catholic emphasis on the Virgin Mary and the saints highlights a broader understanding of intercession and devotion. Catholics view Mary not only as the mother of Jesus but also as a powerful advocate for humanity, deserving of veneration. This practice of seeking the intercession of saints creates a rich tapestry of spiritual support for believers, offering them a sense of connection to the broader history of faith. Together, these elements of authority, sacramental life, and intercessory devotion create a distinct Catholic identity that continues to resonate with millions around the globe.
Faith Foundations: Key Differences in Christian Traditions
Christianity is a diverse faith with a rich tapestry of traditions that shape the beliefs and practices of its followers. At the heart of these differences lie varying interpretations of the Bible, the role of sacraments, and the understanding of salvation. For instance, while Catholics emphasize the importance of tradition and the authority of the Pope, Protestant denominations often prioritize personal scripture interpretation and a direct relationship with God. This fundamental divergence sets the stage for a multitude of expressions within the faith.
In addition to scriptural interpretation, the view of sacraments varies significantly among Christian traditions. Catholics observe seven sacraments as vital channels of grace, while many Protestants recognize only two—baptism and communion—focusing on their symbolic rather than sacramental significance. This distinction not only influences worship practices but also shapes the spiritual lives of believers, underscoring the importance of community and ritual in some denominations while promoting individual faith experiences in others.
Finally, the concept of salvation serves as a critical differentiator among Christian traditions. For Catholics, salvation is a lifelong journey involving faith, good works, and participation in the sacraments, whereas many Protestants advocate the belief in salvation through faith alone, often emphasizing a personal acceptance of Jesus Christ as Lord and Savior. These varying perspectives foster a rich dialogue among Christians, inviting deeper understanding and appreciation of the faith’s multifaceted nature.
Catholicism vs. Christianity: A Closer Look at Core Principles
At first glance, Catholicism and Christianity may appear synonymous, sharing foundational beliefs in Jesus Christ’s life and teachings. However, a closer examination reveals distinct differences in their core principles. Catholicism, as a branch of Christianity, emphasizes the authority of the Pope, the significance of sacraments, and the role of tradition in interpreting Scripture. This structured hierarchy and the sacramental system serve to guide the faithful in their spiritual journey, fostering a deep sense of community and continuity with the Church’s historic roots.
In contrast, many other Christian denominations prioritize personal interpretation of the Bible and the individual’s relationship with God. This emphasis on personal faith and a direct connection to Scripture allows for a broader range of beliefs and practices among Christians. While both Catholicism and other Christian sects share a commitment to the teachings of Christ, their differing approaches to authority, tradition, and community shape unique spiritual experiences that reflect their diverse interpretations of faith.
Bridging the Gap: Exploring Catholic and Christian Faiths
The exploration of Catholic and Christian faiths reveals a rich tapestry of beliefs and practices that share a common foundation in the teachings of Jesus Christ. Both traditions emphasize love, compassion, and the importance of community, fostering a sense of belonging among their adherents. While Catholicism offers a structured hierarchy and sacramental system, various Christian denominations embrace diverse interpretations of scripture and worship styles, creating a vibrant spectrum of faith experiences. This diversity invites dialogue and understanding, encouraging followers to appreciate the nuances that enrich their spiritual journeys.
At the heart of this exploration is the desire to bridge divides and cultivate mutual respect among believers. Engaging in open conversations about shared values, such as the significance of grace and redemption, can create a deeper understanding of each faith’s unique contributions to the broader Christian narrative. By recognizing the common threads that unite them, Catholics and Christians can work together towards a more inclusive and harmonious expression of faith, fostering a sense of unity that transcends doctrinal differences. Through this collaborative spirit, both communities can inspire one another to live out their beliefs with authenticity and purpose.
Common Ground and Divergence: The Catholic Christian Landscape
The Catholic Christian landscape is a rich tapestry woven from shared beliefs and diverse traditions. At its core, the Catholic faith emphasizes the sacraments, the authority of the Pope, and a commitment to community and service. This common ground fosters a sense of unity among believers, encouraging them to practice compassion and uphold moral values rooted in scripture. From vibrant liturgies to community outreach programs, these shared practices create a strong foundation for collective worship and fellowship.
However, within this framework of unity, there is also significant divergence that reflects the varied cultural and historical contexts of Catholic communities around the world. Regional customs, liturgical practices, and interpretations of doctrine can differ widely, giving rise to unique expressions of faith. For instance, the vibrant celebrations of Catholicism in Latin America contrast sharply with the more subdued practices seen in parts of Europe. This diversity enriches the Catholic tradition, allowing it to adapt and thrive in different environments while still maintaining its fundamental tenets.
Understanding the distinction between Catholics and Christians reveals a rich tapestry of beliefs, traditions, and practices that shape the spiritual lives of millions. While all Catholics are Christians, the nuances in doctrine, rituals, and community life highlight the diversity within the broader Christian faith. Embracing these differences fosters a deeper appreciation for the shared values that unite believers, encouraging dialogue and understanding in an increasingly diverse world.