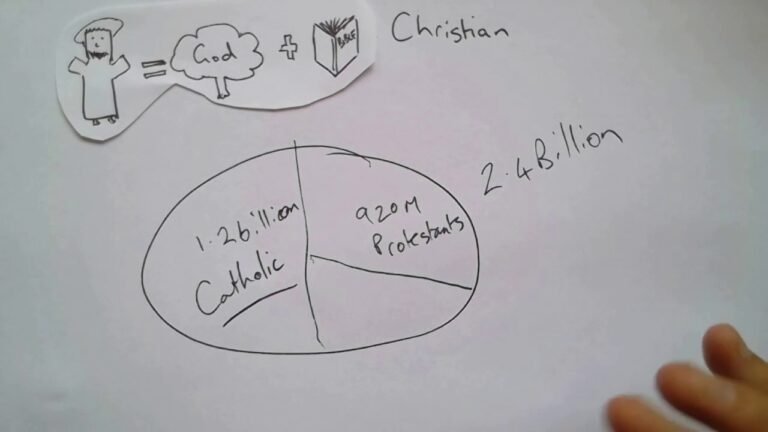
Understanding the Differences Between Christianity and Catholicism
Understanding the distinction between Christianity and Catholicism is essential for grasping the rich tapestry of religious beliefs that shape our world. While all Catholics are Christians, not all Christians are Catholics, as Christianity encompasses a diverse array of denominations and interpretations of faith. This article delves into the fundamental differences in beliefs, practices, and traditions that set Catholicism apart within the broader Christian context, providing clarity on a topic often surrounded by misconceptions.
What distinguishes Christianity from Catholicism?
Christianity is the broad faith encompassing all followers of Christ, while Catholicism is a specific branch with unique beliefs, practices, and traditions within Christianity.
Advantages
- Clarity in Beliefs: Understanding the differences between Christianity and Catholicism can provide clarity regarding distinct beliefs, practices, and interpretations of scripture, helping individuals make informed choices about their faith.
- Enhanced Dialogue: Recognizing the nuances between the two can foster better interfaith dialogue, promoting respect and understanding among different Christian denominations and encouraging collaboration on shared values.
Disadvantages
- Misunderstanding of Beliefs: Many people conflate Christianity and Catholicism, leading to confusion about core beliefs, practices, and traditions. This can result in a lack of clarity regarding the unique aspects of each faith.
- Division Among Followers: The distinction between Christianity and Catholicism can create divisions among followers, sometimes leading to tension or conflict within communities that share a common belief in Jesus Christ.
- Limited Perspective: Focusing solely on the differences may hinder a deeper understanding of the shared values and teachings of both Christian denominations, resulting in a narrow view of faith that overlooks common ground.
- Stereotyping: Differences can lead to stereotypes about Catholics or other Christian denominations, fostering misconceptions and prejudices that may prevent constructive dialogue and mutual respect among believers.
What distinguishes Catholicism from Christianity?
Roman Catholicism stands out among Christian denominations primarily due to its unique beliefs regarding sacraments and the interplay between Scripture and tradition. While all Christians acknowledge the significance of the Bible, Catholics place equal weight on the teachings and traditions of the Church, which they believe have been passed down through the centuries. This dual foundation shapes their understanding of faith and practice, leading to distinct rituals and a specific approach to worship.
Additionally, the veneration of the Virgin Mary and the saints is a hallmark of Catholicism that sets it apart from other Christian groups. Catholics believe that these figures intercede on their behalf, enriching their spiritual lives and providing models of holiness. Furthermore, the papacy plays a critical role in Catholicism, serving as the central authority that guides the Church’s teachings and maintains unity among believers. This combination of elements creates a rich tapestry of faith that is both unique and deeply rooted in tradition.
Do Catholics and Christians worship the same God?
The concept of a shared God is a cornerstone of the ecumenical movement, which aims to foster unity among diverse Christian denominations. This belief suggests that despite varying interpretations and practices, all branches of Christianity, including the Roman Catholic Church, are fundamentally worshiping the same divine presence. This perspective encourages dialogue and collaboration among different faith communities.
While theological differences may exist, the fundamental recognition of a common God serves as a bridge for understanding. It highlights the shared values and beliefs that unite Christians, emphasizing love, compassion, and the pursuit of truth. Such a foundation can lead to meaningful conversations about faith, promoting a sense of solidarity among believers.
Ultimately, the idea that Catholics and other Christians share the same God invites a spirit of inclusivity and respect. It encourages congregations to focus on what unites them rather than what divides them, fostering a more harmonious and cooperative approach to faith in a diverse world. Through this lens, the potential for unity becomes a powerful force for positive change within and beyond faith communities.
Is Jesus a Christian or a Catholic?
Jesus, who lived from approximately 6 to 4 BC to AD 30 or 33, is recognized as a pivotal figure in history, known as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth. As a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader, he laid the foundational teachings that would eventually give rise to Christianity, now the world’s largest religion. While he is central to the faith, Jesus himself was a Jew and did not identify as a Christian or Catholic, as these terms emerged long after his lifetime.
Unveiling Core Beliefs: A Comparative Study
In exploring the intricate web of human values, this comparative study delves into the core beliefs that shape diverse cultures around the globe. By examining fundamental principles such as individualism versus collectivism and the role of spirituality in everyday life, we uncover the driving forces that influence societal norms and personal behaviors. This analysis not only highlights the rich tapestry of beliefs that exist but also fosters a deeper understanding of how these values impact interpersonal relationships and community dynamics.
As we unveil these core beliefs, it becomes evident that while differences may abound, there are universal threads that connect us. Empathy, respect, and the quest for meaning resonate across cultures, suggesting that despite our varied backgrounds, we share a common humanity. This study encourages an appreciation for both the uniqueness of individual belief systems and the shared values that can bridge gaps, promoting harmony in an increasingly interconnected world.
Key Distinctions Explained: Faith and Practice
Faith and practice are two interrelated concepts that form the foundation of many belief systems. Faith is often described as a deeply held conviction or trust in something greater than oneself, whether it be a deity, a philosophy, or a set of principles. It serves as the internal compass that guides individuals through life’s challenges, providing them with a sense of purpose and direction. This personal belief is often nurtured through experiences, teachings, and reflections, creating a rich tapestry of spiritual understanding.
On the other hand, practice encompasses the actions and rituals that manifest one’s faith in the real world. It includes behaviors, traditions, and community engagements that allow individuals to express their beliefs outwardly. Whether through prayer, meditation, charitable acts, or participation in communal gatherings, practice is the embodiment of faith in daily life. It transforms abstract beliefs into tangible actions, fostering a sense of belonging and shared identity among like-minded individuals.
The distinction between faith and practice is clave for understanding how beliefs influence behavior. While faith can exist independently as a personal conviction, practice requires active participation and commitment. Together, they create a dynamic interplay that shapes individual and collective experiences. Recognizing this relationship allows people to explore their beliefs more deeply, encouraging a holistic approach to spirituality that integrates both internal convictions and external expressions.
Bridging Faiths: What Sets Them Apart?
In a world rich with diverse beliefs, the exploration of faith serves as a bridge connecting different cultures and communities. While each religion offers unique traditions and teachings, they often share common threads, such as the pursuit of truth, moral guidance, and a sense of belonging. Understanding these distinctions and similarities not only fosters mutual respect but also encourages dialogue that transcends boundaries. By appreciating the nuances of each faith, we can cultivate a deeper understanding of our shared human experience.
At the heart of these differences lies the interpretation of the divine and the role of humanity in the cosmos. Some faiths emphasize individual relationships with a higher power, while others focus on communal practices and rituals. This divergence shapes the values and ethical frameworks of their followers, influencing everything from daily choices to life-altering decisions. By examining what sets these beliefs apart, we invite a richer conversation about spirituality, allowing us to learn from one another and build a more harmonious world.
Exploring Doctrinal Divergences: A Clear Guide
In the realm of religious studies, doctrinal divergences often serve as a lens through which we can better understand the complexities of faith and belief systems. By examining the fundamental differences that exist among various religious traditions, we uncover not only the unique tenets that define each faith but also the shared values that foster dialogue and understanding. This exploration reveals the intricate tapestry of beliefs that shape human experience, prompting us to reflect on the reasons behind our convictions and the potential for common ground.
Navigating these differences can be both illuminating and challenging, as each doctrine carries its own historical context and cultural significance. A clear guide through these divergent paths encourages open-mindedness and respect, enabling us to engage in meaningful conversations about faith. By appreciating the richness of diverse perspectives, we can cultivate a more inclusive environment that honors individual beliefs while also celebrating the unity that can emerge from our shared quest for truth and understanding.
Navigating the Divide: Insights into Two Traditions
In a world rich with cultural diversity, the interplay between contrasting traditions reveals profound insights into human experience. On one side, we find the structured, hierarchical practices that emphasize community and continuity, often rooted in ancient customs. These traditions serve as a framework for social cohesion, offering individuals a sense of belonging and identity. They remind us of our shared history and values, creating bonds that transcend generations.
Conversely, the more fluid and adaptive traditions highlight the importance of innovation and personal expression. These approaches encourage individuals to challenge norms and embrace change, often leading to vibrant artistic and social movements. By prioritizing individual creativity and adaptability, these traditions foster environments where new ideas can flourish, ultimately enriching the cultural landscape. The dynamic tension between these two philosophies invites us to explore the complexities of our identities and the world around us.
Navigating this divide requires a nuanced understanding of both traditions, recognizing their unique contributions to society. By engaging with the strengths of each, we can cultivate a more inclusive dialogue that honors heritage while embracing progress. This synthesis not only deepens our appreciation for cultural diversity but also equips us with the wisdom to address contemporary challenges, forging pathways that honor the past while inspiring a brighter future.
Understanding the differences between Christianity and Catholicism enriches our appreciation of the diverse beliefs that shape our world. While both share core tenets of faith in Jesus Christ, they diverge in practices, traditions, and interpretations of scripture. Recognizing these distinctions fosters respectful dialogue and deeper connections among believers, highlighting the beauty of faith in its many forms.