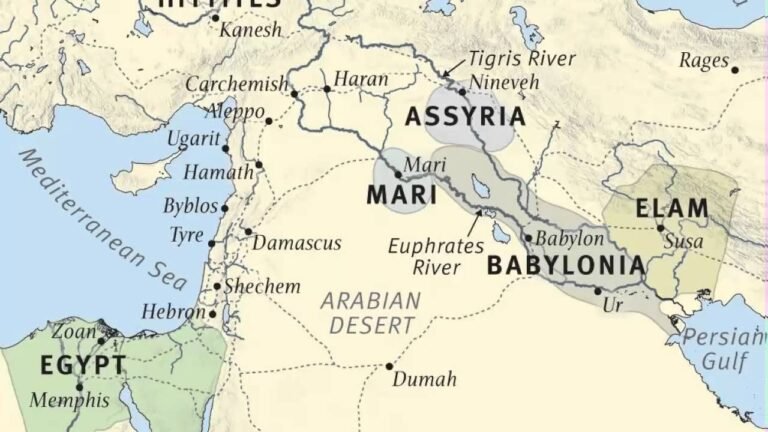
Mapping the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers: A Historical Overview
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers, two of the most significant waterways in the Middle East, have shaped the landscape, culture, and history of the region for millennia. A detailed map of these rivers reveals their winding paths through modern-day Iraq, Syria, and Turkey, highlighting the fertile lands that once cradled ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia. Understanding the geography of the Tigris and Euphrates not only illuminates the past but also underscores their continuing importance in contemporary environmental and geopolitical discussions.
In which region can the Tigris and Euphrates rivers be found?
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers, two of the most significant waterways in the Middle East, originate in eastern Turkey, just 50 miles apart. These ancient rivers have played a decisivo role in the development of civilizations, providing fertile land and essential resources to the regions they traverse.
As they flow southeast, the Tigris and Euphrates carve their way through northern Syria and Iraq before they converge at the head of the Persian Gulf. This journey not only shapes the geography of the area but also supports diverse ecosystems and communities, making these rivers vital to the history and culture of the region.
What events occurred between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers?
The region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, often referred to as the cradle of civilization, has undergone significant ecological changes in recent years. The Euphrates, once a vital water source for the surrounding marshlands, has seen parts of its flow diverted to the sea. This redirection has had devastating effects on local ecosystems and communities that depend on the rivers for their livelihoods.
In response to the dwindling water supply, a dam was constructed to prevent water from the Tigris from backing up and replenishing the marshlands. This decision, while aimed at managing water resources, has exacerbated the environmental crisis in the region. The once-thriving wetlands, rich in biodiversity, have steadily diminished, leading to increased salinity and a loss of habitat for many species.
To further accelerate the drying process, some marshlands were deliberately burned, and underground pipes were installed to facilitate the rapid removal of water. These actions reflect a troubling trend in the management of water resources, prioritizing short-term gains over the long-term health of the ecosystem. The consequences of these changes serve as a stark reminder of the delicate balance required to sustain both human and environmental needs in this historically significant area.
Which countries are home to the Tigris and Euphrates rivers?
The Euphrates and Tigris rivers are vital waterways that traverse the heart of the Middle East, primarily flowing through Turkey, Syria, and Iraq. These rivers have historically supported agriculture, drinking water, and ecosystems, making them essential for the livelihoods of millions. Their basin not only nurtures the land but also serves as a lifeline for the cultures and economies of the regions they touch.
In addition to Turkey, Syria, and Iraq, Iran plays a significant role by encompassing parts of the Tigris basin. The interdependence of these nations on the rivers underscores the complexity of their shared resources. As populations grow and demands increase, the management of these waters has become a source of contention, highlighting the need for cooperative agreements to ensure sustainable usage.
Since the 1960s, unilateral irrigation projects have altered the natural flows of the Euphrates and Tigris, exacerbating political tensions among the riparian countries. The impact of these changes has not only affected agriculture and water availability but has also led to disputes over rights and responsibilities. As these nations navigate the challenges of resource management, the future of the Euphrates-Tigris basin hinges on dialogue and collaboration to foster peace and prosperity for all involved.
Unveiling the Cradle of Civilization
Nestled between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Mesopotamia stands as one of humanity’s earliest cradles of civilization. This fertile land, often referred to as the “land between the rivers,” was home to pioneering cultures that laid the foundations for agriculture, writing, and urbanization. The Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians thrived here, creating complex societies that developed monumental architecture, intricate legal codes, and remarkable advancements in science and mathematics. Their innovations not only transformed their world but also set the stage for future civilizations.
As we delve into the rich tapestry of Mesopotamian history, we uncover the profound impact these ancient peoples had on the course of human development. From the invention of cuneiform script to the establishment of city-states, their legacy continues to resonate today. This region’s cultural achievements fostered trade and communication, ultimately shaping the trajectory of societies far beyond its borders. Understanding Mesopotamia is essential for appreciating the interconnectedness of our shared past and the enduring influence of its remarkable contributions to civilization.
Charting Ancient Waterways: Past Meets Present
Throughout history, waterways have played a pivotal role in shaping civilizations, serving as vital arteries for trade, transportation, and communication. Ancient cultures harnessed the power of rivers and lakes, building intricate networks that facilitated commerce and cultural exchange. From the Nile in Egypt to the Indus River Valley, these waterways were not just lifelines; they were the very foundation of societal development, enabling agriculture, urbanization, and the rise of powerful empires.
In the modern era, the significance of these ancient routes is being rediscovered as cities and countries seek sustainable solutions for growth. Advances in technology have allowed for the mapping and analysis of these waterways, revealing their historical importance and ecological value. By understanding the past, contemporary societies can implement innovative strategies for water management, ensuring that these resources continue to support economic and environmental goals.
As we chart the ancient waterways, we bridge the gap between past and present, recognizing that the lessons learned from our ancestors can guide us toward a sustainable future. Emphasizing conservation and responsible usage, we can honor the legacies of those who relied on these vital resources while adapting to the challenges of modern life. By weaving together history and innovation, we can create a harmonious relationship with our waterways, ensuring they thrive for generations to come.
The Lifeblood of Mesopotamia: A Geographic Journey
Flowing through the heart of ancient Mesopotamia, the Tigris and Euphrates rivers were not just waterways; they were the lifeblood of a thriving civilization. Their fertile banks nurtured agriculture, allowing early societies to flourish and innovate, leading to the rise of monumental cities such as Babylon and Ur. This geographic journey reveals how the ebb and flow of these rivers shaped the cultural, economic, and social landscape, fostering trade and communication across vast distances. As the cradle of civilization, Mesopotamia stands as a testament to the profound impact of geography on human development, where water transformed arid lands into a vibrant hub of activity and creativity.
The Tigris and Euphrates rivers, depicted vividly on maps, are not merely geographical features but the lifeblood of ancient civilizations and modern landscapes alike. Their intertwining paths tell stories of growth, conflict, and resilience, shaping cultures and economies for millennia. Understanding their significance through detailed maps not only enriches our knowledge of history but also highlights the ongoing relevance of these waterways in contemporary discussions about environmental sustainability and regional development. As we navigate the complexities of the present, the legacy of the Tigris and Euphrates continues to inspire and inform our journey forward.